Your cart is empty
Looks like you haven't added anything to your cart yet
Types of Bariatric Surgery: Comparing Weight-loss Surgery Options
Bariatric surgery is a term that encompasses various surgical procedures designed to help individuals with severe obesity achieve significant and sustained weight loss. The primary goal of these surgeries is to reduce the size of the stomach, limit food intake, and, in some cases, alter the digestive process to decrease the absorption of calories and nutrients.
Weight-loss surgery is often recommended for individuals with a body mass index (BMI) of 40 or higher, or those with a BMI of 35 or higher who also have obesity-related health conditions like type 2 diabetes, sleep apnea, or high blood pressure.
Types of Weight-Loss Surgery
Gastric Bypass (Roux-en-Y)
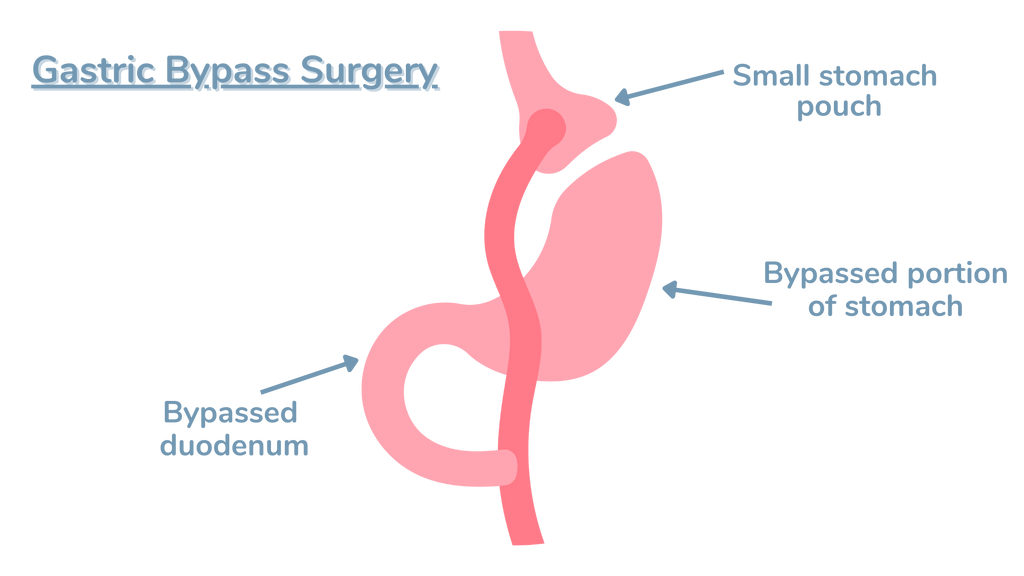
Gastric bypass, also known as Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, is one of the most common and effective types of bariatric surgery. This procedure involves creating a small pouch at the top of the stomach and connecting it directly to the small intestine, bypassing most of the stomach and the upper part of the small intestine.
During the surgery, the surgeon staples a portion of the stomach to create a small pouch, typically about the size of an egg. This pouch is then connected to the middle section of the small intestine (jejunum), allowing food to bypass the rest of the stomach and the upper part of the small intestine (duodenum).
By creating a smaller stomach pouch, gastric bypass drastically reduces the amount of food a person can consume at one time, leading to a feeling of fullness more quickly. Additionally, bypassing a portion of the small intestine results in decreased absorption of calories and nutrients.
Advantages:
- Significant and sustained weight loss, with patients typically losing 60-80% of their excess body weight
- Improvement or resolution of obesity-related health conditions like type 2 diabetes, sleep apnea, and high blood pressure
- Reduced risk of obesity-related cancers and cardiovascular diseases
Disadvantages:
- Requires significant lifestyle changes, including adherence to a strict diet and vitamin supplementation
- Higher risk of complications compared to less invasive procedures
- Potential for nutrient deficiencies due to decreased absorption
Potential complications and risks:
- Anastomotic leaks (leaks at the surgical connections)
- Internal hernias
- Bowel obstruction
- Dumping syndrome (rapid emptying of stomach contents into the small intestine)
- Gallstones
- Ulcers
Despite the potential risks and complications, gastric bypass remains one of the most effective and widely performed bariatric surgeries, offering significant weight-loss and improvement in obesity-related health conditions for many patients.
Other Recommended Guides:
Sleeve Gastrectomy
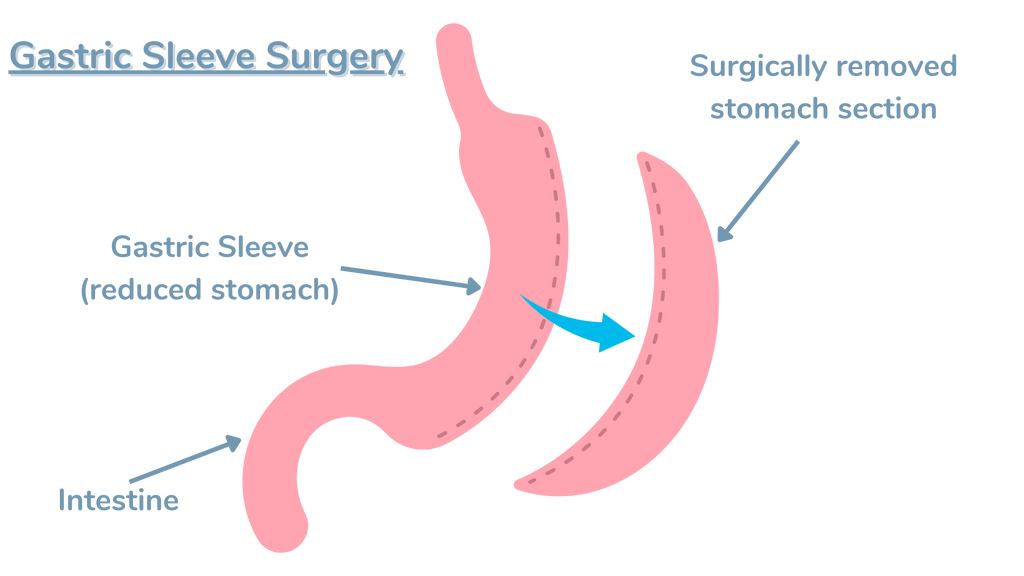
Sleeve gastrectomy, also known as vertical sleeve gastrectomy, is a newer type of bariatric surgery that has gained popularity in recent years. This procedure involves removing approximately 80% of the stomach, leaving a thin, sleeve-shaped stomach about the size and shape of a banana.
During the surgery, the surgeon uses staples to divide the stomach vertically, creating a small, tubular pouch. The remaining portion of the stomach is then removed. By reducing the size of the stomach, sleeve gastrectomy limits the amount of food a person can consume, leading to a feeling of fullness more quickly and reducing overall calorie intake.
Unlike gastric bypass, sleeve gastrectomy does not involve rerouting the intestines, which means the normal absorption of nutrients and calories remains largely unchanged.
Advantages:
- Significant weight loss, with patients typically losing 50-60% of their excess body weight
- Improvement or resolution of obesity-related health conditions
- Lower risk of nutrient deficiencies compared to gastric bypass
- Shorter hospital stay and recovery time compared to more invasive procedures
Disadvantages:
- Non-reversible procedure, as a portion of the stomach is permanently removed
- Potential for weight regain over time
- Higher risk of acid reflux and heartburn compared to other bariatric procedures
Potential complications and risks:
- Leaks along the staple line
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Blood clots
- Strictures (narrowing of the sleeve)
Sleeve gastrectomy has become an increasingly popular choice for bariatric surgery due to its relative simplicity, shorter recovery time, and effective weight loss results. However, as with any surgical procedure, it is essential for patients to carefully consider the potential risks and lifestyle changes required before deciding to undergo sleeve gastrectomy.
Adjustable Gastric Banding (Lap-Band)
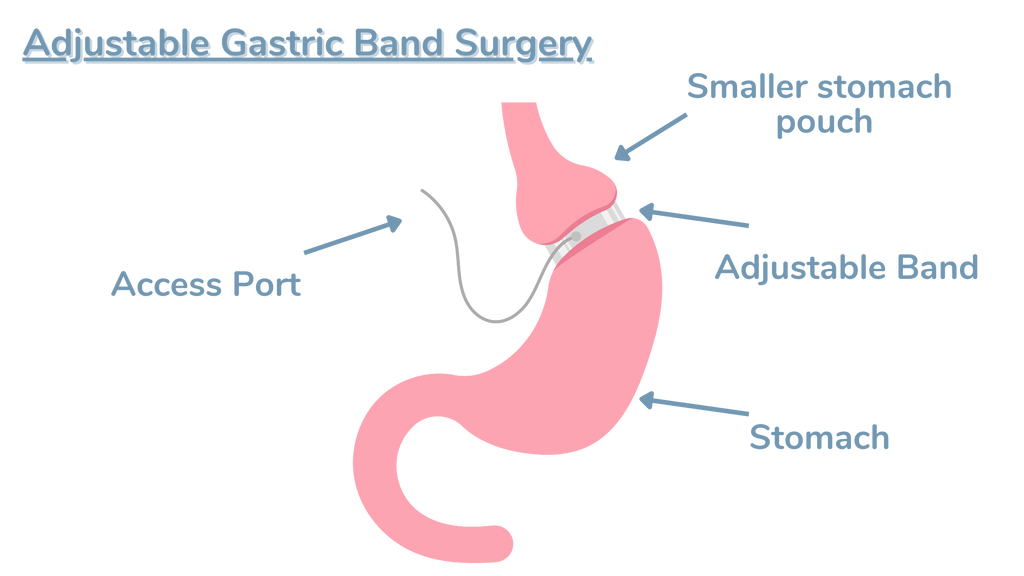
Adjustable gastric banding, also known as Lap-Band surgery, is a reversible bariatric procedure that involves placing an adjustable silicone band around the upper portion of the stomach. This band creates a small pouch at the top of the stomach, limiting the amount of food that can be consumed and slowing its passage into the rest of the digestive tract.
The band is connected to a port placed under the skin of the abdomen, which allows the surgeon to adjust the tightness of the band by adding or removing saline solution. These adjustments help control the size of the stomach opening and the rate at which food passes through, ultimately leading to a feeling of fullness and reduced calorie intake.
Advantages:
- Least invasive bariatric procedure
- Reversible and adjustable
- Shortest hospital stay and recovery time
- Lowest risk of vitamin and mineral deficiencies
Disadvantages:
- Slower and less dramatic weight loss compared to other bariatric procedures
- Requires frequent follow-up visits for band adjustments
- Higher risk of band-related complications, such as slippage or erosion
- Potential for weight regain if the band is removed
Potential complications and risks:
- Band slippage or migration
- Band erosion into the stomach
- Esophageal dilation
- Port-related complications (infection, leakage, or dislocation)
While adjustable gastric banding offers a less invasive and reversible option for bariatric surgery, it has become less popular in recent years due to its lower weight loss efficacy and higher risk of long-term complications compared to other procedures. Nonetheless, it remains a viable option for some patients, particularly those who prefer a reversible procedure or have contraindications for more invasive surgeries.
Biliopancreatic Diversion with Duodenal Switch (BPD/DS)
Biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch (BPD/DS) is a complex and less commonly performed bariatric surgery that combines both restrictive and malabsorptive elements. This procedure involves removing a portion of the stomach (similar to sleeve gastrectomy) and rerouting the small intestine to limit calorie and nutrient absorption.
During the surgery, the surgeon first performs a sleeve gastrectomy to reduce the size of the stomach. Next, the small intestine is divided, and the end portion (ileum) is connected to the duodenum (the first part of the small intestine), bypassing the majority of the intestine. This rerouting significantly reduces the absorption of calories, fat, and nutrients.
Advantages:
- Greatest weight loss potential, with patients typically losing 70-80% of their excess body weight
- Highly effective in resolving obesity-related health conditions, particularly type 2 diabetes
- Allows for larger meal portions compared to other bariatric procedures
Disadvantages:
- Highest risk of nutritional deficiencies due to the malabsorptive nature of the procedure
- Requires strict adherence to dietary guidelines and lifelong vitamin and mineral supplementation
- Longer hospital stay and recovery time compared to other procedures
- Higher risk of complications and mortality compared to other bariatric surgeries
Potential complications and risks:
- Malnutrition and vitamin deficiencies
- Protein-calorie malnutrition
- Anemia
- Osteoporosis
- Dumping syndrome
- Bowel obstruction
- Gallstones
Due to its complexity and potential for serious complications, BPD/DS is typically reserved for patients with severe obesity (BMI > 50) or those who have failed to achieve adequate weight loss with other bariatric procedures. Patients who undergo BPD/DS require close monitoring and lifelong follow-up care to manage nutritional deficiencies and other potential complications.

Eligibility for Bariatric Surgery
Generally, bariatric surgery is recommended for individuals who meet the following criteria:
- A BMI of 40 or higher, which is considered severe obesity
- A BMI of 35 or higher, along with one or more obesity-related health conditions such as type 2 diabetes, sleep apnea, high blood pressure, or heart disease
- Inability to achieve and maintain significant weight loss through conventional methods like diet and exercise
In addition to meeting these BMI and health criteria, candidates for bariatric surgery must also undergo a comprehensive pre-surgery evaluation. This evaluation typically includes:
- A thorough medical examination to assess overall health and identify any potential risks or complications
- A psychological assessment to ensure the individual is mentally prepared for the lifestyle changes required after surgery
- Nutritional counseling to discuss dietary changes and requirements before and after the procedure
Once a person has been deemed eligible for bariatric surgery, they will work closely with their healthcare team to determine which type of procedure is best suited to their individual needs and goals.
Here's a yearly statistical overview of each procedure.
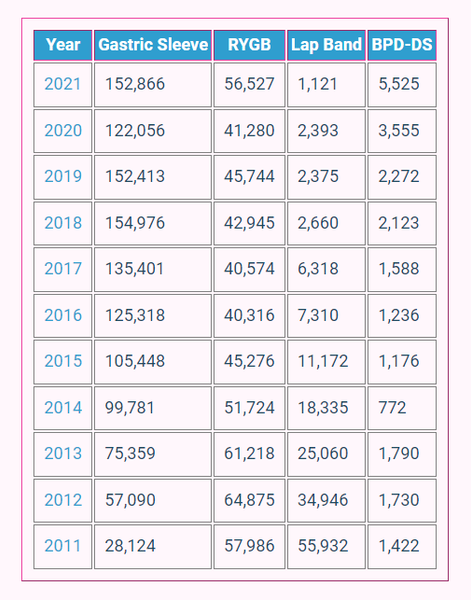
Conclusion
The four main types of bariatric surgery – gastric bypass, sleeve gastrectomy, adjustable gastric banding, and biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch – each offer unique advantages and disadvantages, as well as varying degrees of weight loss and potential risks.
It is important to remember that bariatric surgery is not a quick fix or a cosmetic procedure, but rather a serious medical intervention that requires significant lifestyle changes and lifelong commitment. If you are considering bariatric surgery, it is important to consult with a qualified healthcare professional who can help you understand the risks, benefits, and lifestyle changes associated with each procedure.
Writer: Allison Allison, a certified nutritionist and research author, brings over 15 years of experience in the health and weight loss industry. Allison's influence extends through her authorship of multiple health and wellness journals, where she shares her expertise and research on medical weight loss and bariatric medicine. |
Reviewed By: Dr. K. Huffman Dr. Kevin D. Huffman, D.O., is a board-certified bariatric physician renowned for his expertise in treating obesity. With over 10,000 patients and a reputation as a national leader in bariatric medicine, he has trained hundreds of healthcare providers. As the founder of American Bariatric Consultants, Dr. Huffman develops protocols and training materials sought after by medical societies, pharmaceutical companies, patients, and hospitals. |
- Choosing a selection results in a full page refresh.










