Your cart is empty
Bariatric Surgery Risks, Complications & Side Effects
Complete Evidence-Based Guide to Understanding Weight Loss Surgery Risks in 2025
🧭 Quick Navigation
Understanding Bariatric Surgery Risks
Comprehensive Risk Assessment
While bariatric surgery risks are generally low compared to other major surgeries, understanding potential complications is crucial for making an informed decision. Weight loss surgery complications can range from minor side effects to serious medical emergencies, and they may occur immediately after surgery or develop years later. This guide examines all major risks of bariatric surgery based on the latest medical evidence.
Critical Statistics You Need to Know
💡 Key Points About Bariatric Surgery Safety
- Overall Safety: 96% of patients have no major complications
- Mortality Comparison: Safer than gallbladder surgery and knee replacement
- Experience Matters: Surgeon expertise dramatically impacts outcomes
- Long-term Benefits: Often outweigh surgical risks for qualified candidates
- Prevention Focus: Many complications are preventable with proper care
Immediate Post-Surgery Risks (0-30 Days)
First 24-48 Hours
Critical Period: Most serious complications occur early
- Anastomotic leaks: Most serious complication (1-5% risk)
- Bleeding: Internal or external bleeding requiring intervention
- Pulmonary embolism: Blood clots traveling to lungs
- Anesthesia complications: Breathing problems, allergic reactions
First Week
Early Recovery Issues
- Wound infections: Surgical site complications
- Deep vein thrombosis: Blood clots in legs
- Dehydration: Due to reduced stomach capacity
- Nausea and vomiting: Common digestive adjustments
First Month
Short-term Adaptations
- Strictures: Narrowing of surgical connections
- Dumping syndrome onset: Rapid food transit symptoms
- Food intolerance: Difficulty digesting certain foods
- Gallbladder issues: Stones from rapid weight loss
The most critical period for complications is the first 48 hours after surgery. This is when we see the most serious issues like leaks and blood clots. The good news is that with experienced surgical teams and proper monitoring, these risks are very manageable.
Dr. Kevin Huffman, Bariatric Physician
Procedure-Specific Risks Comparison
🔴 Gastric Bypass (Roux-en-Y)
Gastric Bypass Side Effects:
- Dumping syndrome (85% of patients)
- Nutritional deficiencies (highest risk)
- Internal hernias (2-5% lifetime risk)
- Marginal ulcers (1.5 per 100 patient-years)
- Hypoglycemia (late dumping)
Gastric Bypass Surgery Side Effects - Long Term:
- Vitamin B12 deficiency (30-35%)
- Iron deficiency anemia (up to 50%)
- Bone density loss
- Alcohol sensitivity increase
🟡 Sleeve Gastrectomy
Sleeve Surgery Complications:
- Staple line leaks (1-3%)
- Gastroesophageal reflux (new or worsened)
- Sleeve stenosis (narrowing)
- Barrett's esophagus (11.6% risk)
Long-term Concerns:
- Acid reflux progression
- Need for revision surgery
- Nutritional deficiencies (lower than bypass)
🟢 Gastric Band (LAP-BAND)
Band-Specific Complications:
- Band slippage or erosion
- Port complications
- Band removal needs (high rate)
- Insufficient weight loss
Note: Less commonly performed due to higher revision rates and lower long-term success.
🔵 Duodenal Switch
Complex Procedure Risks:
- Highest nutritional deficiency risk
- Protein malnutrition
- Frequent diarrhea
- Complex revision surgeries
- Liver complications
Reserved for highest BMI patients due to complexity.
Long-Term Complications and Side Effects
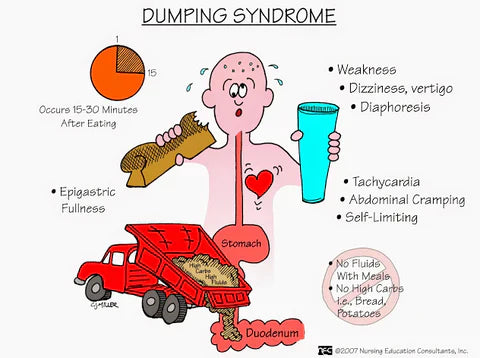
Dumping syndrome affects up to 85% of gastric bypass patients and occurs when food moves too quickly from the stomach to the small intestine.
Early Dumping (15-30 minutes after eating)
- Nausea and vomiting
- Abdominal cramping
- Diarrhea
- Rapid heart rate
- Sweating and dizziness
Late Dumping (1-3 hours after eating)
- Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar)
- Tremors and shakiness
- Confusion
- Rapid heart rate
- Sweating
📊 Long-term Complication Rates
Understanding the likelihood of various long-term effects helps set proper expectations:
- Nutritional deficiencies: 5x more common than general population
- Gallstone formation: 20-25% of patients
- Hernias requiring surgery: 2-5% lifetime risk
- Bowel obstruction: 1-3% of patients
- Revision surgery needs: 5-15% depending on procedure
Nutritional Deficiencies - The Hidden Risk
One of the most significant weight loss surgery side effects is the development of nutritional deficiencies. These complications are 5 times more common in bariatric surgery patients compared to the general population.
| Nutrient | Deficiency Rate | Symptoms | Prevention |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vitamin B12 | 30-35% within 1 year | Fatigue, neurological issues, anemia | Monthly injections or high-dose oral supplements |
| Iron | Up to 50% (especially women) | Anemia, fatigue, weakness, hair loss | Iron supplements with vitamin C |
| Calcium | 25-50% | Bone loss, osteoporosis, fractures | Calcium citrate + Vitamin D |
| Vitamin D | 50-80% | Bone weakness, muscle pain | High-dose vitamin D supplements |
| Folate | 10-20% | Anemia, neural tube defects in pregnancy | Daily folate supplements |
| Thiamine (B1) | 5-15% | Neurological problems, heart issues | B-complex vitamins |
⚠️ Why Nutritional Monitoring is Critical
Bariatric surgery permanently alters your digestive system's ability to absorb nutrients. Regular blood work and lifelong supplementation aren't optional - they're essential for preventing serious health complications that can develop years after surgery. Following proper dietary guidelines and choosing appropriate bariatric food options specifically formulated for post-surgery needs can significantly reduce the risk of nutritional deficiencies.
Major Surgical Complications Requiring Intervention
| Complication Type | Occurrence Rate | Severity Level |
|---|---|---|
| Gallstones | 20-25% | Moderate |
| Strictures | 10-15% | Moderate |
| Marginal Ulcers | 5-8% | High |
| Internal Hernia | 2-5% | High |
| Bowel Obstruction | 1-3% | High |
🚨 Life-Threatening Complications
- Anastomotic leaks (1-5%)
- Pulmonary embolism (leading cause of death)
- Severe bleeding requiring transfusion
- Sepsis from infection
- Liver failure (rare, long-term)
⚠️ Serious but Treatable
- Internal hernias requiring surgery
- Bowel obstructions
- Marginal ulcers
- Severe strictures
- Chronic dehydration
ℹ️ Manageable Complications
- Dumping syndrome
- Food intolerances
- Mild strictures
- Gastroesophageal reflux
- Minor wound infections
Risk Mitigation and Prevention Strategies
🏥 Pre-Surgery Risk Reduction
- Choose experienced, board-certified surgeon
- Select ASMBS-accredited center
- Optimize medical conditions pre-surgery
- Quit smoking 6+ weeks before surgery
- Achieve required pre-surgery weight loss
- Complete psychological evaluation
✅ Post-Surgery Prevention
- Follow dietary guidelines strictly
- Take bariatric supplements religiously
- Attend all follow-up appointments
- Stay hydrated (64+ oz water daily)
- Exercise regularly as cleared
- Monitor for warning symptoms
👥 High-Risk Patient Factors
- BMI over 50 kg/m²
- Previous abdominal surgeries
- Heart or lung disease
- Diabetes with complications
- Sleep apnea
- Blood clotting disorders
- Age over 65
💡 Choosing the Right Surgical Team
Surgeon experience dramatically impacts outcomes. Look for:
- High volume: Surgeons performing 100+ procedures annually
- Low complication rates: Ask for center-specific statistics
- Comprehensive program: Dietitians, psychologists, support groups
- Emergency capabilities: 24/7 access to surgical team
- Long-term follow-up: Lifelong care commitment
When to Seek Emergency Help
🚨 Emergency Symptoms - Call 911 Immediately
- Severe abdominal pain that doesn't improve with rest
- Chest pain or shortness of breath (possible blood clot)
- Persistent vomiting unable to keep fluids down for 24+ hours
- Signs of infection: fever over 101°F, chills, rapid heart rate
- Severe dehydration: dizziness, dark urine, confusion
- Leg pain and swelling (possible deep vein thrombosis)
- Difficulty breathing or chest tightness
📞 Contact Your Surgeon for These Symptoms
- Persistent nausea lasting more than 24 hours
- Inability to tolerate solid foods for several days
- Severe dumping syndrome symptoms
- Signs of nutritional deficiency (fatigue, hair loss, weakness)
- Unexpected weight regain or weight loss stalling
- Changes in bowel habits or severe diarrhea
- Wound healing problems or discharge
Never hesitate to contact your surgical team if something doesn't feel right. We'd rather evaluate ten false alarms than miss one serious complication. Early intervention can prevent minor issues from becoming major problems.
Dr. Kevin Huffman, Bariatric Physician
Benefits vs. Risks: The Complete Picture
While risks of weight loss surgery are real, studies consistently show that benefits outweigh risks for qualified candidates:
✅ Consider Surgery If You Have:
- BMI ≥40 or BMI ≥35 with comorbidities
- Failed multiple weight loss attempts
- Obesity-related health problems
- Commitment to lifelong lifestyle changes
- Realistic expectations about outcomes
- Strong support system available
❌ Consider Alternatives If You Have:
- Untreated eating disorders
- Severe mental health issues
- Inability to commit to follow-up care
- Unrealistic weight loss expectations
- Active substance abuse
- Prohibitive surgical risks
📈 Long-term Success Statistics
- Weight Loss Success: 90% maintain 50%+ excess weight loss
- Diabetes Improvement: 75% experience remission
- Blood Pressure: 60% see significant improvement
- Sleep Apnea: 80% experience improvement or resolution
- Quality of Life: 95% report improved quality of life
- Patient Satisfaction: 85-95% would choose surgery again
Frequently Asked Questions About Bariatric Surgery Risks
What is the death rate from bariatric surgery?
The mortality rate for bariatric surgery is approximately 0.1%, making it safer than many common surgeries including gallbladder removal and knee replacement. The risk varies by procedure type and patient health status.
Which bariatric surgery has the lowest complication rate?
Gastric sleeve surgery generally has lower immediate complication rates than gastric bypass, while gastric banding (LAP-BAND) has the lowest immediate risks but higher long-term revision rates due to poor effectiveness.
How common are long-term complications after weight loss surgery?
Long-term complications vary by procedure, but nutritional deficiencies are the most common, affecting up to 50% of patients who don't maintain proper supplementation and regular follow-up care. Most complications are preventable with proper management.
What are the most serious risks of gastric bypass surgery?
The most serious gastric bypass risks include anastomotic leaks (1-5%), pulmonary embolism, severe nutritional deficiencies, and internal hernias requiring emergency surgery. However, these occur in less than 5% of patients overall.
Can bariatric surgery complications be prevented?
Many complications can be prevented or minimized through proper surgical technique, careful patient selection, adherence to post-operative guidelines, regular follow-up care, and choosing an experienced surgical team at a high-volume center.
What are the long-term side effects of gastric sleeve surgery?
Long-term gastric sleeve side effects include gastroesophageal reflux (new or worsened), potential development of Barrett's esophagus (11.6%), nutritional deficiencies (though less than bypass), and possible need for revision surgery in some patients.
How do I minimize my risk of complications?
Minimize risk by choosing an experienced surgeon at an accredited center, optimizing your health pre-surgery, following all dietary guidelines, taking supplements as prescribed, attending follow-up appointments, and maintaining open communication with your medical team.
Are the benefits worth the risks for most patients?
For qualified candidates with severe obesity, studies consistently show that the benefits significantly outweigh the risks. Bariatric surgery reduces overall mortality by 41% and dramatically improves obesity-related health conditions in most patients.
Making an Informed Decision About Bariatric Surgery
Understanding bariatric surgery complications is essential, but these risks must be weighed against the significant health risks of remaining severely obese. With proper surgical selection, experienced teams, and committed post-operative care, the vast majority of patients experience life-changing benefits that far outweigh the risks.
Key Takeaways: Overall risk is low (96% have no major complications) • Benefits often outweigh risks for qualified candidates • Long-term follow-up is crucial • Choose experienced providers • Lifestyle commitment required for success
Disclaimer: This guide is for educational purposes only. Always consult with qualified healthcare providers for personalized medical advice. Individual results and risks may vary based on your specific health status and type of surgery.
Author: Carrie H. Carrie is a passionate health and nutrition writer who transforms complex medical research into accessible, evidence-based content to empower readers to make informed choices about their wellbeing. With a background in science and a dedication to helping others live healthier lives, she provides thoughtful analysis of the latest studies and practical, actionable advice readers can apply to their own lives. |
Reviewed By: Dr. Kevin Huffman Dr. Huffman is an accomplished board-certified bariatric physician with extensive clinical experience and expertise in treating obesity. He has trained countless healthcare providers and founded American Bariatric Consultants to develop highly sought-after protocols, training materials and continuing education used widely by medical societies, hospitals and physicians. Dr. Huffman's impact reaches far beyond direct patient care, as he actively prepares the next generation of physicians to achieve board certification in bariatrics, thereby exponentially expanding access to this vital medical treatment. |
- Choosing a selection results in a full page refresh.